Wireless refers to any electrical or electronic operation that is accomplished without the use of a ‘hard wired’ connection. It gives users a ‘live’ internet connection via satellite or radio transmitters without the use of wires. Mobile means that technology can travel with the user but is not necessarily in real time. Wireless devices, such as Blackberries and iPhones are small enough to carry around and have the ability to store information, perform productive tasks and communicate wirelessly over the internet and with other wireless devices.
The benefits of wireless technology for businesses are;
- Universal access to information and applications – technology is getting to the stage where information is able to be accessed anywhere at any time.
- The automation of business processes – wireless technologies have the ability to centralise critical information and eliminate redundant processes.
- User convenience, timeliness and ability to conduct business 24/7, 365 days a year – information, through wireless technologies such as a Blackberry or iPhone, can be accessed anywhere and at any time.
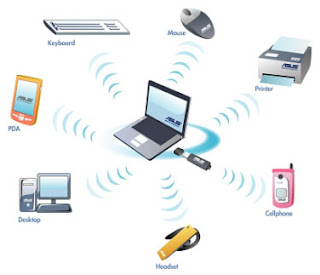
http://www.tentechnologies.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/09/wireless.jpg
2. Describe the business benefits associated with VoIP.
Voice over IP (VoIP) uses TCP/IP technology to transmit voice calls over internet technology. As the calls are transported over the internet, international call costs have decreased. VOIP enables phone calls, faxes, voice mail, email and web conferences to be transmitted over the internet. It also reduces the cost and complexity with delivering these services and improves response and restoration times. With VOIP using existing networks to efficiently and inexpensively route telephone calls, businesses can gain significant cost savings, productivity gains and service enhancements.
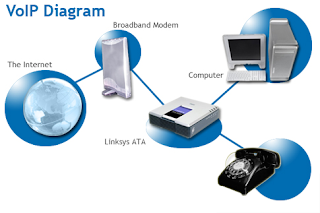
VOIP saves money in 3 ways:
- It runs over the existing computer network
- Calls over the internet do not attract extra telecommunication charges
- Customers are able to port their numbers between carriers
An example of a VOIP is Skype. Skype allows users to send copies of reports, pictures or other files with no size restrictions on files.
3. Compare LANs and WANs.
- LAN – Local area networks connect a group of computers within a close proximity of each other to be able to share resources like files, games, printers and other applications. An LAN can connect to other LANs to the internet or wide area networks.
Example of a LAN:
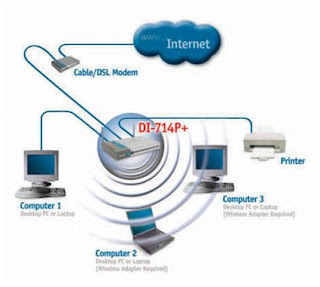
http://www.internet-computer-checkup.com/image-files/wireless-lan-router.jpg
- WAN – Wide area networks are networks that span over a larger distance, such as a state or country.
Example of a WAN:
.gif)
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/Cc751420.wan_msp01_big(en-us,TechNet.10).gif
4. Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technologies use active or passive tags in the form of chips or smart labels that store unique identifiers and relay this information to electronic readers. RFID tags are smaller than a grain of sand and combine tiny chips with an antenna, which, when placed on an item, automatically radios its location to RFID readers on shop shelves, counters, loading bay doors and shopping carts. They can cut cost by reducing the number of workers required for scanning items and can provide current and more accurate information to the entire supply chain. They have allowed businesses to reduce costs and overheads by making inefficient business systems more visible and are being used to improve the cost, safety and reliability of managing business processes.

No comments:
Post a Comment