The three primary variables within any project are time, cost and scope. All projects are limited by one of these variables in some way. These three variables are interdependent and the relationship is that if a change is made to one variable, it is likely to affect one or all of the other variables. It is these three factors that determine the quality of a project with a successful project delivered on time, within the determined budget and according to the scope originally set out during the planning stages.

Triple Constraints Diagram
http://www.traue.com/media/project_triangle.png
2. Describe the two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning.
The two primary diagrams used in project planning are;
· PERT Chart: A PERT (Program Evaluations and Review Technique) chart is a graphical diagram that presents are projects tasks and the relationship between those tasks. A dependency is a logical relationship that exists between two tasks or between a task and a milestone. They define dependency between project tasks before they are scheduled. The critical path is the path to completing the project in the shortest amount of time.

Example of a Pert chart
http://www.spottydog.u-net.com/images/fancy_pert.jpg
· Gantt Chart: A Gantt Chart is depicted in the form of a bar graph against a calendar. The tasks to be completed are listed vertically and the time frame they must be completed in is listed horizontally. A Gantt chart shows the schedule of a project and the progress of the tasks against their planned duration.

Example of a Gantt chart
http://www.total-quality-management-software.com/images/project_gantt_chart.gif
3. Identify the three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success.
The three primary areas a project manager must focus on to manage success are;
· People: This is the hardest but most important task of a project manager. Two challenges that are faced are resolving conflict within the group and balancing the needs of the project with the personal and professional needs of the group. Project managers are the main communicators with the client. In many cases it is the people management side of the project that determines the success of the project. A project manager needs to manage the stakeholders as well as the team members of a project. It is important for a project manager to correctly manage the stages of the group (forming, storming, norming, performing and adjourning) as this can also determine the success of a project.
· Communications: Communication is the key to excellent project management. A project manager should plan what and how they will communicate as a formal part of the project management plan. The project manage should communicate to the team the time, cost and scope of the project in a timely, accurate and meaningful fashion, as well as keeping all stakeholders informed of the progress of the project. Project managers should also monitor feedback and respond in a timely and organised manner, as well as encouraging group members to provide feedback.
· Change: A project manager needs to be able to anticipate, monitor and prepare for change to occur. Change management is a set of techniques that aid in evolution, composition and policy management of the design and implementation of a system. It includes a collection of procedures to document a change request and the steps necessary to consider the change based on the expected impact of the change.
Three guidelines for effectively dealing with change management are:
1. Institute change management policies – clearly define the policies and procedures that must be followed each time a request for change is made.
2. Anticipate change – view change as an opportunity and embrace it.
3. Seek change – look for changes that may be a window to opportunity. Review successes and failures to determine for any opportunities to innovation.
4. Outline 2 reasons why projects fail and two reasons why projects succeed.
Why projects succeed:
· All team members working towards the common goal of the project
· Good decision making structure and communication, e.g. project can be completed within project timeline and all members are aware of their role within the project and are kept regularly informed.
Why projects fail:
· Unrealistic expectations of the project, e.g. too short a timeline, not enough resources available, too large for the company to handle.
· Lack of project management, e.g. no project manager guiding the project, no project plan developed (PERT or Gantt chart)

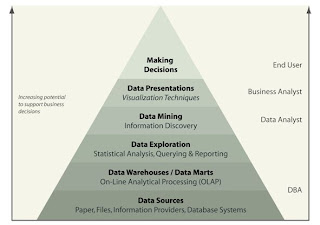 Business Intellogence Diagram
Business Intellogence Diagram


.gif)





